Nowadays, arthritis disease has become the most common disease in all pathologies of the musculoskeletal system. In addition, urban residents, people who are accustomed to a sedentary lifestyle, and people who have recently suffered injuries of varying degrees of intensity, most often suffer from joint diseases.
In this regard, the doctor’s forecast is disappointing. It is speculated that in the near future, the number of people suffering from various forms of large joint arthritis will only increase. According to the latest data, about 7% of people have experienced all the symptoms and consequences of arthritis.
The disease has become one of the main causes of disability and performance degradation. There is a characteristic that the peak incidence occurs in the age group of 40 to 60 years, and not only elderly pensioners, which is wrongly believed.
What is arthropathy?
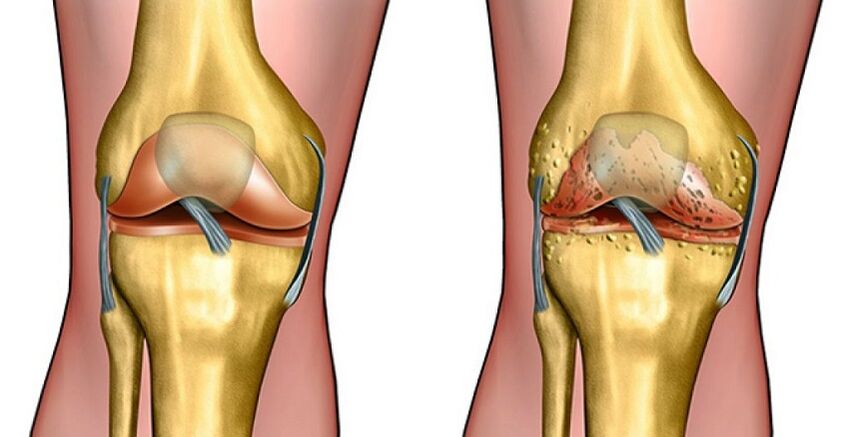
Arthritis (another name for osteoarthritis) should be understood as a complex degenerative pathology in which the cartilage plates of the bones that form the joints are destroyed. The reason is not only the process that occurs in hyaline cartilage.
There are many other prerequisites for the disease.
Joint arthritis develops in the following situations:
- Excessive physical exercise. Usually, in this case, overweight people get sick. Human joints are not suitable for continuous exercise with heavy loads. Therefore, the increased pressure on the knee during the activity is a prerequisite for minimal trauma to the cartilage tissue. Violates the sliding properties of tissues and reduces joint mobility. Athletes often suffer high loads due to the rapid and frequent changes in the natural pressure between the joint surfaces or insufficient heating of the joints, resulting in damage to the joint system;
- Congenital or acquired deformities, injuries to the musculoskeletal system. In this case, insufficient contact between the joint surfaces of the bones can cause disease. The entire load must not be distributed on the joints, and damage will result in excessive compression. Violation disease, scoliosis and kyphosis are obvious examples. It should also include improper fusion of fractures and various deformities of limbs;
- Violation of cartilage regeneration. In the case of inflammatory processes in the body, impaired blood circulation and hormonal destruction, the mechanism of the development of this arthritis can be observed. The problem is due to insufficient recovery of cartilage tissue, lack of natural remodeling and thinning.
- Synovial fluid formation and problems. In the case of insufficient joint fluid, the friction surface will continue to be injured, wear and inflammation will accelerate, and the overall condition of the body will deteriorate.
Stages of arthritis
Since the disease causes destruction of articular cartilage tissue, its symptoms vary greatly depending on the stage of the pathological process.
Due to the active destruction of the joint surface, a person will develop new symptoms, and the prognosis of regaining exercise capacity will not change. According to the clinical condition of the disease, the doctor will choose the best treatment method and medicine.
First-degree arthritis is characterized by discomfort and slight soreness only after prolonged strenuous exercise. After a short rest, the signs that appeared during physical exercise gradually disappeared.
In this case, the joint pathology is not visible on the X-ray photograph, but the joint space may be slightly reduced.
The second stage of pathology is characterized by increased symptoms. Now it is not only caused by long-term activities, but also caused by slight movements of the limbs.
Rest will not bring the desired relief. Movement has rigidity, and the mobility of joints is restricted. It is recommended to reduce the load on the affected joints at this time, but it should not be completely eliminated, otherwise muscle atrophy will occur. X-rays will show obvious joint signs:
- Bone growth
- deformation;
- Vegetation (osteophytes) near the joint space, which narrows.
When the disease reaches its final stage, the lesions in the joints will produce constant and intense pain. Therefore, at the reflex level, a person begins to sharply restrict their movement to protect the affected joints from stress. When the joints are at rest, pain syndrome can occur even during sleep and rest.
The patient was forced to adopt the least harmful posture. You can only move with the help of a wheelchair or crutches.
The characteristic is that the third and fourth degree joints will completely deprive a person of the ability to walk due to the fusion of the articular surface (stiffness).
Which joint is most easily affected?
According to medical statistics, the lower limbs are most susceptible to joint disease. The joints suffer from inflammation and degeneration: hips, knees.
In the unlikely event that there is a problem with the hip joint, after a long time of walking or running, you will initially feel pelvic pain. With the active development of pathology, pain intensifies and mobility is restricted.
A person will find that the stiffness of the joints is not good, and in certain positions, the stiffness will increase several times at a time. In the final stage of hip arthritis, the patient will subconsciously protect the affected leg and try not to step on it. He does not move his pelvis, which helps to relieve pain.
Discomfort and soreness after walking is manifested as arthritis of the knee joint. There are no problems and external manifestations of inflammation. The most common prerequisite for knee arthritis is the trauma it has suffered in the past against the background of internal structural damage.
Usually, this damage causes an abnormality in the abutment of the contacted joint surface. At the same time:
- Overload certain areas of cartilage;
- Their rapid wear and tear.
As mentioned earlier, changes depend on the degree of joints. You should also consider the cause of the disease, appropriate medical services, the general condition of the body, and the dynamics of the pathological process. Certain forms of illness will not leave you in a state of discomfort for a long time and will not progress.
Sometimes, even for decades, the knee has not significantly deteriorated. In other cases, symptoms will increase rapidly and the possibility of incapacity is high.
Get rid of joint disease
Nowadays, there are two main directions in the treatment of arthritis of the large joints: medicine and surgery.
First of all, the purpose of treatment is to quickly improve the blood circulation of diseased joints and accelerate the characteristics of cartilage tissue with the help of drugs. Anesthesia and inflammation are also needed. For this, doctors practice using the following drugs.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
These drugs interfere with the natural chemical chain in the cartilage that causes inflammation. During exercise, the tissue swells, soreness, and cartilage strength decreases.
Due to the use of anti-inflammatory drugs, the pain syndrome can be reduced or stopped completely. It also prevents the initiation of the so-called chain-like inflammatory process, which helps to accelerate the regeneration of the affected area.
The medicine is produced in the form of tablets, powders and rectal suppositories. Treatment strategy, the choice of specific drugs is determined by the doctor strictly according to the clinical conditions of the disease, its dynamics and accompanying pathological conditions, and according to individual circumstances.
Opioids and chondroprotective agents
Strong central painkillers are called opioids. Usually, such drugs have anesthetic effects on the body and increase the threshold of pain sensitivity. Through this treatment, the pain in the affected area can be reduced.
The use of this group of drugs should be strictly under the supervision of the attending physician, because such drugs can cause mental and physical dependence.
In order to accelerate the recovery of cartilage tissue, special means-chondroprotective agents are used. In general, they are the structural elements of cartilage itself, which makes them have an activating effect on its recovery.
These drugs include:
- Chondroitin sulfate;
- Glucosamine sulfate;
- Hyaluronic acid.
Chondroitin and glucosamine are organic substances abundant in the space between chondrocytes. The mechanism of its action on joints is not yet fully understood, but it has been repeatedly proven that it has a positive effect on the regeneration of cartilage tissue during treatment.
Chondroitin drugs can activate the production of special substances (proteoglycans and hyaluronic acid) in the extracellular matrix of cartilage. At the same time, the absorption process in the tissue is significantly inhibited. Similarly, it can inhibit certain chemical processes, reduce cartilage inflammation, damage and the severity of pain syndromes.
Usually need long-term use of this group of drugs. A course of treatment takes at least 6 months. Otherwise, the benefits of therapy should not be expected. The organic combination of chondroitin and glucosamine is a more common practice. However, clinical studies have not yet confirmed that there is a significant difference between this treatment and the use of only one chondroprotective agent.
Despite the obvious benefits and safety, but due to the relatively high cost, not everyone can use this drug to treat joint arthritis.
Hyaluronic acid is also common in modern medicine. It is a long chain of carbohydrates, which provides elasticity and viscosity to synovial fluid. The unique properties of hyaluronic acid largely determine the good sliding properties of joint fluid.
Intra-articular injection of the drug has a good effect on the physical condition, because studies have shown that the formation of joints is usually caused by the decrease of the concentration of hyaluronic acid in the joint and the shortening of its molecular chain.